M&A Due Diligence Process: A Comprehensive Guide for 2026
The M&A due diligence process is a critical step in any merger or acquisition transaction. It involves a thorough investigation and analysis of a target company's business, conducted by potential buyers or investors to evaluate the viability and risks associated with the deal. Whether you're a company preparing for acquisition or an investor evaluating a potential target, understanding the due diligence process is essential for making informed decisions and ensuring a successful transaction.
In this guide, we'll explore:
- What M&A Due Diligence is
- Why it's important for both buyers and sellers
- How to create a successful due diligence process
- Best practices for maximizing outcomes and minimizing risk
M&A due diligence is a comprehensive investigation and analysis of a target company's business, conducted by potential buyers to evaluate the viability and risks associated with a potential acquisition or merger.
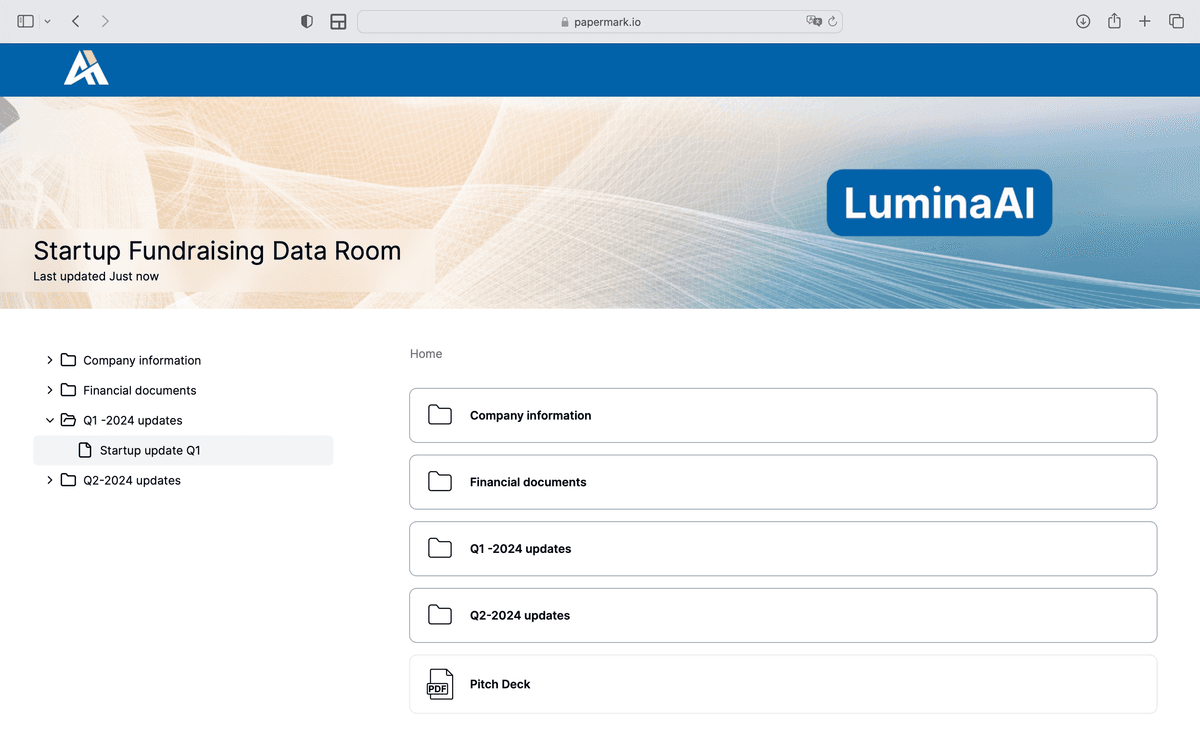
Summary of M&A Due Diligence
- Definition: M&A Due Diligence refers to the investigative process of verifying and assessing a target company's legal, financial, operational, and market position before finalizing acquisition or merger decisions.
- Key Benefits: An effective due diligence process leads to:
- Risk Reduction: Identifies red flags early on
- Valuation Accuracy: Helps align on fair company value
- Stronger Relationships: Builds trust through transparency
- Typical Phases: A thorough due diligence usually includes:
- Primary (Preliminary Review): Collecting basic documentation and establishing rapport
- Secondary (In-Depth Analysis): Diving deep into legal, financial, and operational metrics
- Tertiary (Final Negotiations & Closing): Negotiating terms, clarifying outstanding points, and finalizing the deal
What is M&A Due Diligence?
M&A Due Diligence is the systematic process of confirming key details about a target company's viability, market position, operational efficiency, and legal standing. This verification process is crucial before any significant acquisition or merger. Both buyers and sellers benefit from a well-managed due diligence:
- Buyers: Gain clarity on the company's stability, growth potential, and financial projections, reducing the risk of unforeseen issues post-acquisition
- Sellers: Can showcase their strengths, attract the right buyers, and address potential gaps proactively
Due diligence encompasses multiple facets:
- Financial: Validating revenue, expenses, and projections
- Legal: Reviewing contracts, intellectual property rights, and regulatory compliance
- Market: Evaluating competitive landscape, customer base, and growth potential
- Operational: Assessing internal processes, team expertise, and product development cycles
A robust M&A due diligence ensures all stakeholders enter the relationship with realistic expectations and a solid foundation for growth.
M&A Due Diligence vs. Traditional Corporate Due Diligence
While due diligence for established corporations and M&A targets shares similarities, there are unique factors at play in M&A transactions:
- Integration Considerations: M&A deals often involve significant operational integration, requiring deeper analysis of systems and processes
- Synergy Assessment: Buyers must evaluate potential synergies and cost savings
- Cultural Fit: Evaluating the compatibility of company cultures is crucial
- Management Assessment: Evaluating the existing management team's ability to execute the post-merger strategy
In contrast, traditional corporate due diligence often focuses on strategic fit, synergies, and integration planning. For M&A, it's a deeper exploration of potential and the integrity of projected growth.
Why is M&A Due Diligence Important?
An effective M&A due diligence process offers multiple advantages:
- Drives Informed Investment Decisions: Buyers can evaluate actual risks versus projected returns, ensuring more accurate valuations
- Enhances Transparency: Companies that provide clear, organized data foster trust and streamline negotiation
- Strengthens Relationships: Detailed reviews encourage open communication, building a long-term, collaborative partnership
- Reduces Post-Acquisition Surprises: Identifying legal, financial, or operational risks upfront prevents costly disputes or restructuring down the line
- Improves Negotiation Terms: Both parties have factual insights to guide fair terms on equity, governance, and control
Real-World Example: How family offices running M&A transactions and due diligence
See how G.P. Loree & Co., a New York family office, manages due diligence for complex transactions and deal documentation:
Tools to Build Your M&A Due Diligence Process
Effective due diligence is not a single event; it unfolds through multiple phases as both the target company and buyer align on key metrics, validate documents, and finalize negotiations.
Primary Phase: Preliminary Review
- Goal: Establish initial trust and gather basic documentation about the target company
- Actions:
- Collect Foundational Data: Corporate registration, cap table, pitch deck
- Overview of Financials: Income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow analysis
- Surface-Level Team Assessment: Management backgrounds, relevant experience, and any known advisors
- Tools:
- Data Room for Due Diligence to organize and store preliminary documents
- Cap Table tool for clear equity distribution

During this phase, it's critical for target companies to demonstrate professionalism. Buyers often decide whether to proceed deeper based on how quickly and accurately initial data is provided. Consider referencing Papermark Terms to ensure all documentation management follows best practices and proper legal guidelines.
Secondary Phase: In-Depth Analysis
- Goal: Verify critical details about the company's financials, market fit, legal liabilities, and operational structure
- Actions:
- Legal Documents: Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA), Shareholder Agreements, intellectual property filings
- Financial Scrutiny: Detailed revenue breakdowns, cost of goods sold, headcount expenses, and financial models
- Market & Customer Validation: Current user base, traction metrics, churn rates, and market expansion plans
- Technology Review: If applicable, an audit of code repositories, architecture, and product roadmap
- Tools:
- Term Sheets for aligning on proposed equity and governance terms
- Analytics platforms to track user engagement, customer LTV (lifetime value), and funnel metrics
This in-depth stage is the heart of due diligence, where additional red flags or strengths emerge. Clear references to documented processes, such as an NDA or well-structured agreements, help both parties maintain transparency.
Tertiary Phase: Final Negotiations & Closing
- Goal: Finalize legal, financial, and operational terms, leading to deal closure or the conclusion of discussions
- Actions:
- Agreement on Valuation & Equity Split: Negotiating ownership percentages, liquidation preferences, and governance structure
- Risk Allocation: Addressing warranties, indemnities, and any known liabilities that might surface later
- Term Sheet Finalization: Refining all key deal points into a consolidated term sheet for signatures
- Post-Acquisition Plans: Aligning on KPIs, board seats, or follow-up funding timelines
- Tools:
- Equity Management solutions to simplify share allocations and investor relations post-deal
- Project management or CRM platforms to track final tasks and coordinate signatures
At this final stage, a robust "closing checklist" is often used to ensure no documents or discussion points go unaddressed. Using a centralized Data Room for Due Diligence remains essential for quick referencing of the final documentation.
M&A Due Diligence Checklist 💫
A well-organized data room is crucial for efficient due diligence. Here's a comprehensive breakdown of the documents you should include:
| Category | Documents | Essential | Nice to Have |
|---|---|---|---|
| Company Summary | Executive Summary | ✔️ | |
| Company Summary | Pitch Deck | ✔️ | |
| Company Documents | Incorporation Documents | ✔️ | |
| Company Documents | Shareholder Agreements | ✔️ | |
| Financial Information | Audited Financial Statements (3-5 years) | ✔️ | |
| Financial Information | Tax Returns (3-5 years) | ✔️ | |
| Financial Information | Financial Projections | ✔️ | |
| Legal Documents | Material Contracts | ✔️ | |
| Legal Documents | Intellectual Property Documentation | ✔️ | |
| Legal Documents | Litigation History | ✔️ | |
| Market Information | Market Analysis Reports | ✔️ | |
| Market Information | Customer Contracts | ✔️ | |
| Operational Information | Organizational Chart | ✔️ | |
| Operational Information | Key Personnel Resumes | ✔️ | |
| ESG Information | Environmental Reports | ✔️ | |
| ESG Information | Sustainability Policies | ✔️ |
How to Create a Successful M&A Due Diligence Strategy
Though the specifics can differ based on industry, business model, and buyer preference, a sound due diligence strategy typically includes the following steps:
1. Define Your Target Audience
- Identify Who Benefits Most: Are you creating a data package for strategic buyers, financial buyers, or private equity firms? Each group has different metrics of interest
- Understand Their Goals: Strategic buyers might focus on synergies and market expansion, whereas financial buyers may look for operational improvements
- Highlight Unique Selling Points: Tailor your data and pitch to the specific type of buyer
2. Set Clear Activation Points
- Determine Milestones: For instance, completing the collection of financial statements or verifying IP might be a key checkpoint
- Link Each Milestone to Specific Actions: After financial validation, you might schedule a call with the finance team or CFO to address open questions
- Assign Responsibility: Ensure each checkpoint has an owner—whether it's the CFO, CTO, or legal counsel—so tasks don't fall through the cracks
3. Map the Company & Buyer Journey
- Visualize Each Stage: From initial outreach to final negotiations, chart out all interactions
- Identify Potential Friction: Common bottlenecks can include delayed legal documents or unorganized financials. Proactively plan solutions to mitigate these
- Prepare Contingencies: If certain documents can't be produced, clarify why. This open communication can salvage trust and keep the process moving
4. Build Personalized Flows
- Segment Your Audience: Different buyer profiles require unique levels of detail
- Design Tailored Experiences: For strategic buyers, high-level traction data might suffice; for financial buyers, detailed operational metrics are essential
- Use Secure Data Rooms: Provide custom access levels. Certain buyers may receive deeper financial details, while others see high-level overviews initially
5. Analyze and Iterate
- Track Metrics: Time to close, number of documents requested, or questions asked per buyer type
- Gather Feedback: Post-deal or post-dismissal feedback from buyers can highlight gaps in your data room or approach
- Continuous Improvement: Tweak your approach to ensure subsequent due diligence rounds become smoother and more compelling
M&A Due Diligence Best Practices
Implement these strategies to make your due diligence process more efficient, transparent, and buyer-friendly:
1. Centralize Documentation Early
- Use a Secure Platform: Storing and organizing all critical files in one place is invaluable. Leverage a Data Room for Due Diligence for real-time collaboration and document sharing
- Categorize Files: Group by Legal, Financial, Marketing, HR, etc. This structure saves time for both parties
2. Maintain Data Hygiene
- Keep Information Current: Nothing frustrates buyers more than outdated or inconsistent data. Regularly update financials and performance metrics
- Label Files Clearly: Adopt consistent naming conventions and version control to prevent confusion
3. Provide Contextual Guidance
- Documentation Summaries: Not all buyers will have the time to read every line of every contract. Provide concise overviews or bullet points highlighting key issues or terms
- Action-Oriented Checklists: Alongside your data room, offer a step-by-step approach for reviewing your documentation
4. Engage Legal Counsel Early
- Prevent Discrepancies: A qualified attorney can highlight potential liabilities, unclear IP rights, or corporate structure issues that might concern buyers later
- Draft Solid Agreements: Use resources like Shareholder Agreements to ensure clarity from day one
5. Offer Interactive Communication
- Virtual Meetings & Live Demos: For tech companies, walk buyers through your product's features in real-time. Seeing is often believing
- Dedicated Q&A Sessions: Build trust by tackling complex or sensitive questions openly and promptly
6. Track Engagement to Remove Friction
- Monitor Document Activity: Tools can show whether a buyer has viewed key files, which pages were reviewed, etc.
- Follow Up Strategically: If critical financial statements remain unopened, offer a brief explanation or highlight them via email
7. Be Proactive About Red Flags
- Disclose Past Setbacks: If you had operational challenges or market setbacks, address them head-on. Buyers appreciate honesty and your lessons learned
- Present Mitigation Strategies: For any unresolved risks (e.g., pending lawsuits, uncertain IP), provide context and proposed solutions
8. Gather and Act on Feedback
- Solicit Opinions: Ask buyers for direct feedback on your data room's clarity or any missing info
- Iterate: Continually refine your approach, so future due diligence cycles run smoother
Methods to Facilitate M&A Due Diligence

Streamline the due diligence journey with solutions and methodologies designed to enhance transparency, collaboration, and organization:
-
- Best For: Centralizing legal, financial, and strategic documents
- Key Features: Access controls, activity tracking, secure file sharing
-
Cap Table & Equity Management
- Ideal For: Maintaining accurate ownership records and simulating future financing scenarios
- Key Features: Real-time updates, scenario modeling, investor-friendly dashboards
-
Project Management Platforms
- Great For: Organizing tasks, setting deadlines, and coordinating with your team, attorneys, and buyers
- Examples: Asana, Trello, Monday.com
-
Legal Document Tools
- References: Shareholder Agreements, Term Sheets, NDA
- Best For: Generating standardized or semi-custom legal documents to maintain compliance and clarity
-
Communication & Collaboration Tools
- Examples: Slack, Microsoft Teams, Zoom
- Purpose: Facilitating quick Q&A, real-time product demos, or group discussions
A Deep Dive into Key Areas of M&A Due Diligence
1. Financial Due Diligence
Financial due diligence confirms that the company's monetary health aligns with its claims. Companies must present accurate, verifiable financial statements, including:
- Profit & Loss Statements (P&L): Clear revenue channels and cost structure
- Balance Sheets: Shows assets and liabilities
- Cash Flow Projections: Outline assumptions behind revenue growth and operating costs
- Use of Funds: Specifically address how investment will be allocated
Real-World Example:
If a company claims $50M in annual recurring revenue (ARR), a buyer will likely request bank statements, invoicing history, or subscription management platform data to verify. Discrepancies in recorded ARR can trigger suspicion, so ensure all accounts are reconciled and consistent.
2. Legal & Regulatory Due Diligence
Legal due diligence mitigates the risk of hidden liabilities or compliance issues. Common elements include:
- Corporate Structure: Review formation documents and governance structure
- Shareholder Agreements: Clarify existing ownership, preference shares, or any special rights
- Intellectual Property (IP) Rights: Document trademarks, patents, or copyrights
- Regulatory Compliance: Industry-specific regulations must be addressed
Real-World Example:
A manufacturing company will need documented environmental compliance certificates and safety records. If any violations exist, clarifying remediation plans is critical to avoid future legal disputes.
3. Market & Customer Due Diligence
Buyers evaluate a company's market potential, current traction, and future growth paths:
- Market Size & Trends: Use credible sources to estimate total addressable market (TAM)
- Customer Pipeline & Churn: Highlight user adoption rates, average revenue per user (ARPU), churn rates, and lifetime value (LTV)
- Competitive Advantage: Document unique selling points or differentiators
Real-World Example:
For a SaaS company, evidence of strong customer retention (e.g., 90%+ renewal rates) can be more persuasive than simply citing the global SaaS market's multi-billion-dollar valuation. Buyers want to see real traction, not just big numbers without context.
4. Operational & Team Due Diligence
The team's expertise, internal processes, and cultural fit often dictate long-term success:
- Management & Team Backgrounds: Showcase relevant work history and successful track records
- Organizational Chart: Buyers want to see if roles are clearly defined
- Development Roadmap: Present a clear milestone-driven plan
- HR Policies & Culture: For scaling companies, an inclusive and ethical culture can be crucial
Real-World Example:
A manufacturing company can highlight that 70% of its management team have industry backgrounds, with key hires from reputable firms. This signals both domain expertise and capacity to handle operational challenges.
5. Technical Due Diligence (for Tech Companies)
Technical due diligence drills into the architecture, scalability, and quality of your product:
- Codebase Quality: Some buyers or their advisors may request code reviews
- Tech Stack: Present an overview of frameworks, hosting environments, and integration layers
- Cybersecurity & Data Protection: Outline how you secure user data and handle vulnerabilities
Real-World Example:
If you run a payment platform, demonstrate your compliance with PCI DSS or other payment industry standards. Also, mention any third-party security audits or penetration testing results.
6. Post-Acquisition Planning
Due diligence doesn't stop once the checks are written. To maintain trust:
- Board Meetings: Plan frequent updates on KPIs and major decisions
- Reporting Cadence: Monthly or quarterly updates on financials and milestones
- Value Creation Plans: Outline specific initiatives for operational improvements and growth
Real-World Example:
After closing a $100M acquisition, a company might schedule monthly check-ins with the buyer to ensure capital is deployed effectively and to troubleshoot early-stage obstacles.
Common Pitfalls in M&A Due Diligence (and How to Avoid Them)
-
Incomplete Documentation: Failing to present all crucial files can create distrust
- Solution: Use a comprehensive due diligence checklist and maintain an updated Data Room for Due Diligence
-
Over-Inflated Projections: Buyers can spot unrealistic numbers
- Solution: Base projections on historical data, credible market research, and achievable growth assumptions
-
Underestimating the Importance of Legal Clarity: Loosely defined IP rights or a messy shareholder structure can derail a deal
- Solution: Consult legal experts early, and use structured documents like clear Shareholder Agreements
-
Lack of Communication: Going silent or taking too long to respond can erode buyer confidence
- Solution: Maintain proactive updates. If documentation is pending, clearly communicate timelines
-
Ignoring Cultural & Team Fit: Dismissing the human aspect can lead to internal friction later
- Solution: Highlight team synergy, conflict resolution protocols, and shared vision
The Role of Trust and Transparency
A hallmark of successful M&A due diligence is the trust that forms between companies and buyers. Transparency builds that trust:
- Openly Address Weaknesses: Every company has risks. Show buyers you're aware and have a plan
- Promptly Correct Mistakes: If you discover an error in your data or statements, clarify as soon as possible
- Welcome Scrutiny: Inviting tough questions signals confidence in your processes and metrics
Real-World Outcome:
Many buyers favor deals with slightly lower returns if they trust the management team over higher potential returns with questionable transparency. Integrity and openness often outweigh uncertain, unverified growth curves.
Ready to Level Up Your M&A Due Diligence?
Explore Papermark Terms and set up your Data Room for Due Diligence to organize critical documents and accelerate your next acquisition.
Creating a Data Room with Papermark
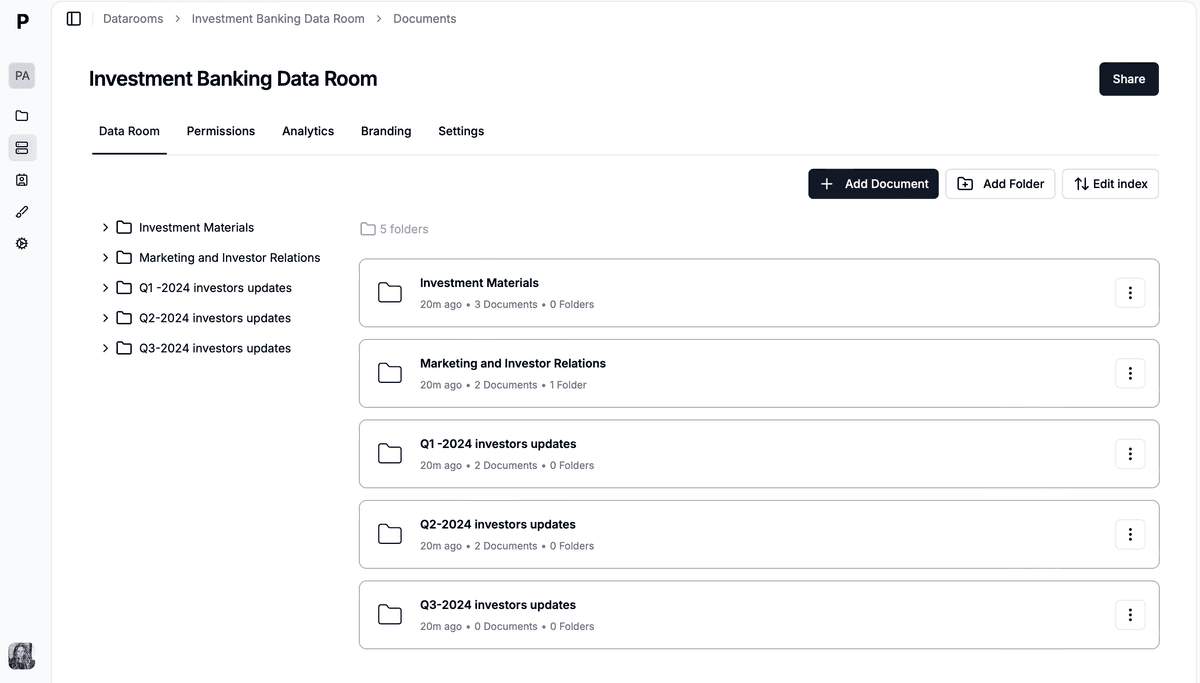
Papermark offers a user-friendly, secure, and cost-effective solution for creating a due diligence data room. Here's how to set up your data room using Papermark:
-
Sign Up: Create an account on Papermark
-
Create a New Data Room:
- Click on "Create New Data Room" in your dashboard
- Name your data room (e.g., "Company Name - Due Diligence 2025")
-
Set Up Folder Structure:
- Create main folders for each category (e.g., Financial, Legal, Market, Product)
- Add subfolders as needed for better organization
-
Upload Documents:
- Drag and drop files into the appropriate folders
- Papermark supports various file formats, including PDFs, spreadsheets, and presentations
-
Configure Access Permissions:
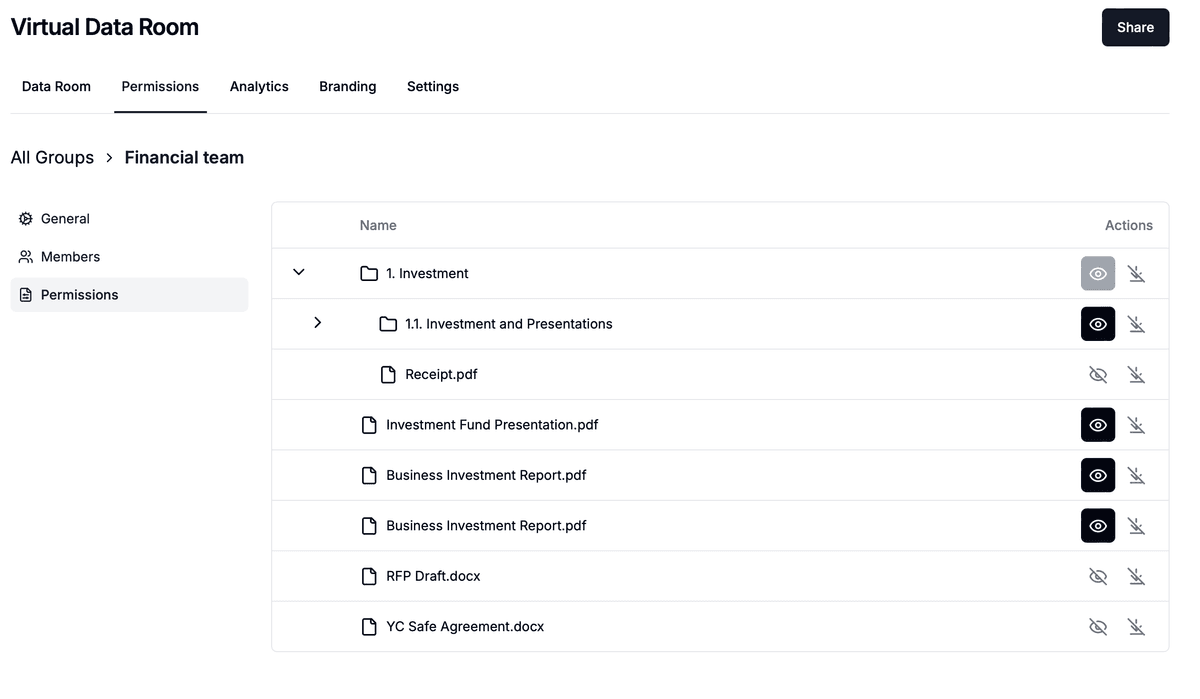
- Set granular access rights for different user groups (e.g., lead buyers, potential investors, advisors)
- Enable or disable download and printing options as needed
- Customize Branding:
- Add your company logo and customize the color scheme to match your brand

-
Enable Security Features:
- Set up two-factor authentication for added security
- Enable document watermarking to protect sensitive information
-
Invite Users:
- Send secure invitations to buyers and other relevant parties
- Provide them with login credentials or allow them to create their own accounts
-
Monitor Activity:

- Use Papermark's analytics dashboard to track user engagement with your documents
- Receive notifications when important documents are viewed or downloaded
Papermark's Unique Features for Due Diligence
Papermark offers several features that make it particularly suitable for M&A due diligence:
- Affordable Pricing: At €59/month, Papermark is significantly more cost-effective than traditional VDR providers
- Unlimited Users and Storage: No need to worry about per-user fees or storage limits
- Dynamic Watermarking: Add user-specific watermarks to sensitive documents for enhanced security
- Customizable NDAs: Require users to sign an NDA before accessing the data room
- Integration Capabilities: Connect with other tools like CRM systems for a seamless workflow
By using Papermark for your due diligence data room, you can ensure a smooth, secure, and professional process that impresses buyers and streamlines the acquisition journey.
Recap of the article
- M&A Due Diligence:
- Importance:
- Key Focus Areas:
- Due Diligence Process:
- Essential Documents:
- Common Pitfalls:
- Buyer Perspective:
- Company Preparation:
- Tools and Resources:
- Best Practices:
For a comprehensive solution to manage your M&A due diligence process, consider Papermark's virtual data room. Our platform offers secure document sharing, customizable permissions, and detailed analytics to streamline your acquisition process.
FAQ
Conclusion
A well-planned M&A Due Diligence strategy sets the stage for long-term success—both for companies seeking acquisition and for buyers aiming to maximize returns. Here's a final recap:
- Identify your audience and their key goals—understand who your buyers are, and tailor documentation to their concerns
- Align the process with core milestones—structure your due diligence into clear phases (primary, secondary, tertiary) to maintain focus and momentum
- Track the journey and adapt—measure each interaction and gather feedback so you can refine future rounds of due diligence
By following these best practices, you not only increase your chances of securing a successful acquisition but also foster a relationship built on clarity, trust, and mutual respect.
