How to send encrypted email in Gmail in 2026
Sending encrypted emails in Gmail is essential for protecting sensitive information like financial documents, legal contracts, or personal data. While standard Gmail uses TLS encryption during transmission, it doesn't provide end-to-end encryption or password protection for your email content. Understanding how to properly encrypt emails in Gmail helps you protect confidential information from unauthorized access.
Gmail offers several methods to enhance email security, from confidential mode to S/MIME encryption. However, for highly sensitive documents, combining Gmail with secure file sharing platforms provides the strongest protection. This guide covers multiple approaches to sending encrypted emails in Gmail, helping you choose the right method for your security needs.
Quick recap of Gmail encryption methods
- Gmail confidential mode: Built-in feature that adds expiration dates and passcode protection
- S/MIME encryption: End-to-end encryption using digital certificates
- Secure file sharing links: Share encrypted documents via secure links instead of attachments
- Password-protected attachments: Encrypt files before attaching to Gmail emails
- Third-party encryption tools: Use additional encryption software for enhanced security
Method 1: Using Gmail confidential mode
Gmail's confidential mode provides basic protection by adding expiration dates and optional passcode requirements to your emails.
Step-by-step guide for Gmail confidential mode:
-
Compose a new email:
- Open Gmail and click "Compose"
- Enter the recipient's email address
- Write your email message
-
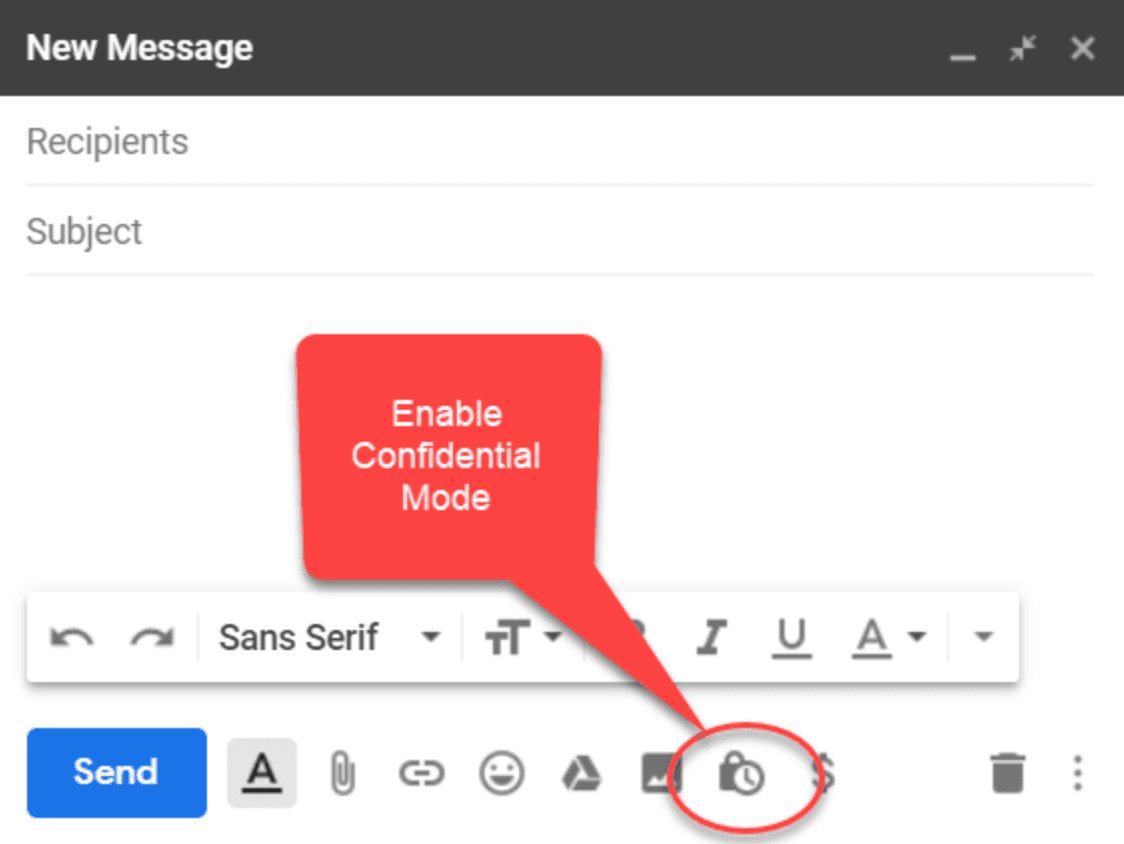
Enable confidential mode:
- Click the padlock icon (🔒) at the bottom of the compose window
- This opens the confidential mode settings

-
Configure expiration settings:
- Set an expiration date for the email (1 day, 1 week, 1 month, 3 months, or 5 years)
- After expiration, the email becomes inaccessible to recipients
-
Set passcode protection (optional):
- Toggle "Require passcode" ON
- Choose "SMS passcode" to send a code via text message
- Recipients must enter this passcode to view the email
-
Send your email:
- Click "Save" to apply confidential mode settings
- Click "Send" to deliver the encrypted email
Important limitations: Gmail confidential mode doesn't provide true end-to-end encryption. Google can still access your email content, and recipients can take screenshots or forward the email. For stronger security, consider encrypting files with passwords before attaching them or using secure file sharing links. Understanding which files need encryption helps you determine when to use additional protection.
Method 2: Using S/MIME encryption in Gmail
S/MIME (Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions) provides true end-to-end encryption for Gmail, ensuring only the intended recipient can read your email.
Step-by-step guide for S/MIME encryption:
-
Obtain a digital certificate:
- Purchase an S/MIME certificate from a trusted Certificate Authority (CA)
- Popular providers include DigiCert, GlobalSign, or Sectigo
- Install the certificate on your computer
-
Enable S/MIME in Gmail (Google Workspace only):
- S/MIME is only available for Google Workspace (formerly G Suite) accounts
- Contact your administrator to enable S/MIME
- Upload your digital certificate in Google Admin Console
-
Compose an encrypted email:
- Compose a new email in Gmail
- Click the lock icon next to the recipient's email address
- If the recipient has S/MIME enabled, you'll see encryption options
- Select "Encrypt" to send an encrypted email
-
Verify encryption status:
- A green lock icon indicates the email will be encrypted
- Both sender and recipient must have S/MIME certificates configured
Note: S/MIME requires both parties to have digital certificates set up. For personal Gmail accounts, S/MIME is not available. Consider using secure file sharing as an alternative for personal accounts.
Method 3: Sending encrypted files via secure links
Instead of attaching files directly to Gmail, you can share encrypted documents through secure links that provide stronger protection and tracking capabilities.
Step-by-step guide for secure file sharing:
-
Upload your file to a secure platform:
- Use Papermark or another secure file sharing service
- Upload your sensitive document
- The file is automatically encrypted with AES-256 encryption
-
Configure security settings:
- Enable password protection for the document
- Set access expiration dates if needed
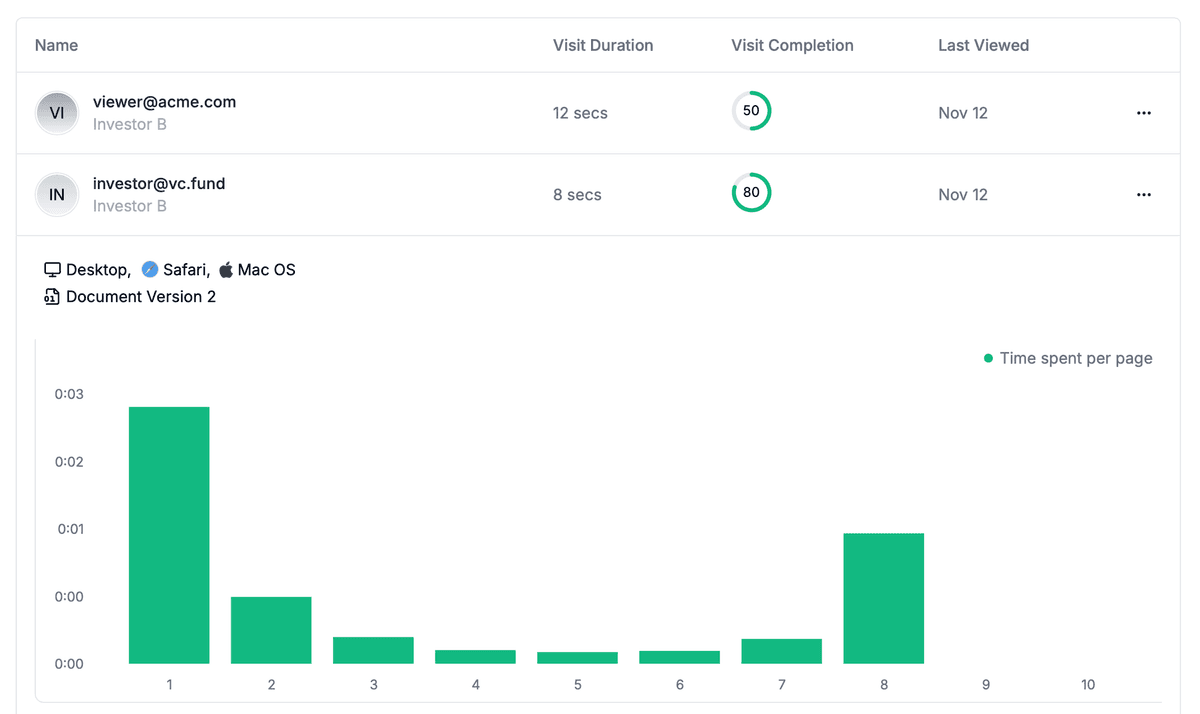
- Enable email verification to require recipient identity confirmation
- Configure allowlist/denylist to control who can access

-
Generate secure link:
- Copy the secure document link from the platform
- The link format typically looks like:
https://www.papermark.com/view/[unique-id]
-
Compose your Gmail email:
- Open Gmail and compose a new email
- Paste the secure link in the email body
- Write a message explaining what the link contains
- Do not include the password in the email
-
Share password separately:
- Send the password through a different channel:
- Phone call
- Text message
- Encrypted messaging app (Signal, WhatsApp)
- In-person communication
- Send the password through a different channel:
Benefits: This method provides stronger encryption than Gmail's built-in features, includes access tracking and analytics, and allows you to revoke access even after sending the email. Learn more about which files need encryption to determine when to use this approach.
Method 4: Password-protecting attachments before sending
You can encrypt files before attaching them to Gmail emails, providing an additional layer of security.
Step-by-step guide for password-protected attachments:
-
Encrypt your file:
- Use built-in encryption tools:
- Word documents: Use Word's "Encrypt with Password" feature
- PDF files: Use Adobe Acrobat's password protection
- Archives: Create password-protected ZIP files using 7-Zip
- For detailed instructions, see our guides on how to encrypt Word files and how to encrypt a file with a password
- Use built-in encryption tools:
-
Set a strong password:
- Create a password with at least 16 characters
- Use a mix of uppercase, lowercase, numbers, and special characters
- Use a unique password for each file
-
Attach encrypted file to Gmail:
- Compose a new email in Gmail
- Click the attachment icon (📎)
- Select your encrypted file
- Write your email message
-
Share password separately:
- Never include the password in the same email
- Send the password through a different communication channel
- Verify the recipient's identity before sharing the password
Security note: While this method encrypts the file itself, the email subject and body remain unencrypted. For maximum security, combine this with Gmail confidential mode or use secure file sharing links.
Comparison: Gmail encryption methods
| Method | Encryption level | Ease of use | Availability | Best for |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gmail confidential mode | Basic (not true encryption) | Very easy | All Gmail accounts | Basic privacy, expiration control |
| S/MIME encryption | End-to-end encryption | Moderate (requires setup) | Google Workspace only | Enterprise email encryption |
| Secure file sharing links | AES-256 encryption | Easy | All accounts | Sensitive documents with tracking |
| Password-protected attachments | File-level encryption | Easy to moderate | All accounts | Individual file protection |
Best practices for encrypted Gmail
Follow these practices to maximize the security of your encrypted Gmail communications.
-
Use strong passwords: When password-protecting files or using confidential mode passcodes, create strong, unique passwords. Never reuse passwords across different files or accounts.
-
Share passwords separately: Always share passwords through a different channel than the email containing the link or attachment. Use phone calls, text messages, or encrypted messaging apps.
-
Enable two-factor authentication: Protect your Gmail account with two-factor authentication (2FA) to prevent unauthorized access to your email account.
-
Verify recipient identity: Before sending sensitive encrypted emails, verify the recipient's email address and identity to ensure you're sending to the correct person.
-
Use secure file sharing for sensitive documents: For highly sensitive files like financial documents or legal contracts, use secure file sharing platforms that provide encryption, access controls, and tracking capabilities. Before sharing, ensure you understand which files need encryption to protect sensitive information properly.
-
Set appropriate expiration dates: Use expiration dates for time-sensitive information. Gmail confidential mode allows you to set expiration dates, and secure file sharing platforms offer similar features.
-
Monitor access when possible: Use platforms that provide access analytics to track who viewed your encrypted files and when. This helps identify unauthorized access attempts.
-
Keep software updated: Ensure your Gmail app, browser, and any encryption tools are kept up to date with the latest security patches.
Conclusion
Sending encrypted emails in Gmail requires understanding the available options and their limitations. Gmail confidential mode provides basic protection for less sensitive information, while S/MIME offers true end-to-end encryption for Google Workspace users. For highly sensitive documents, combining Gmail with secure file sharing platforms provides the strongest protection with encryption, access controls, and detailed tracking capabilities.
Choose the encryption method that matches your security needs, and always follow best practices like sharing passwords separately and verifying recipient identities. For comprehensive file encryption with advanced security features, consider using platforms like Papermark that combine encryption with password protection, access controls, and detailed analytics.